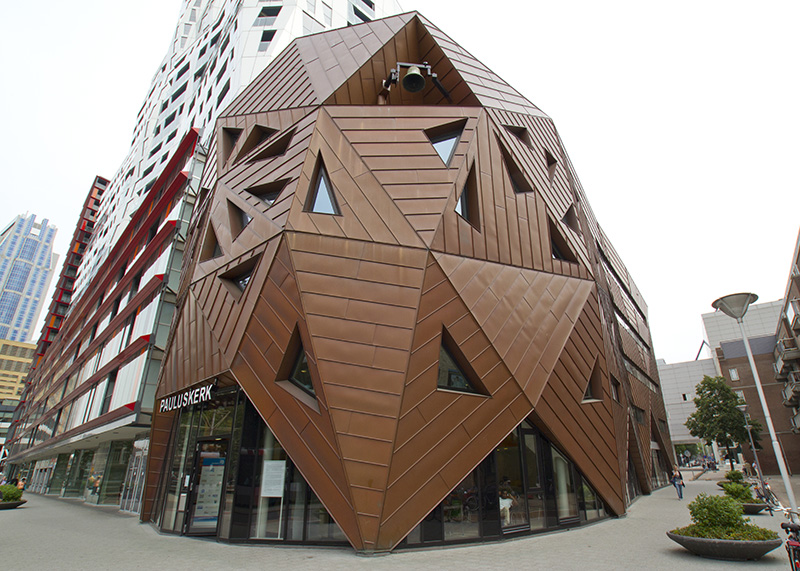
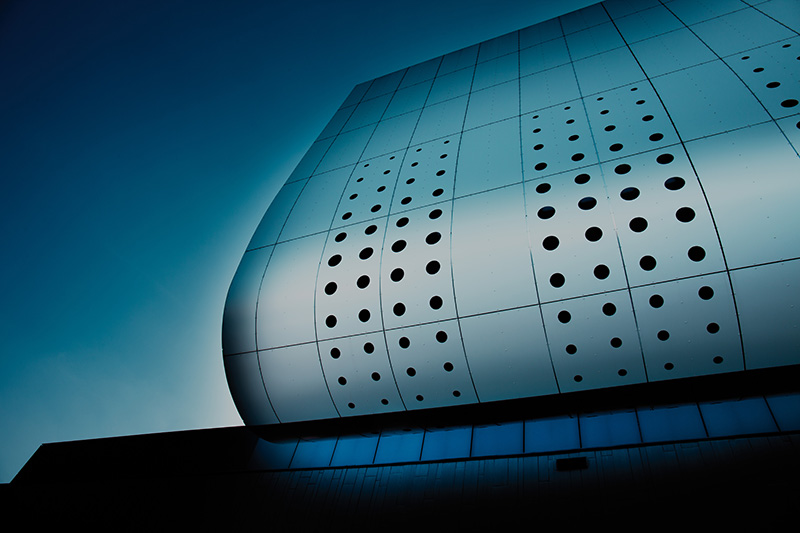
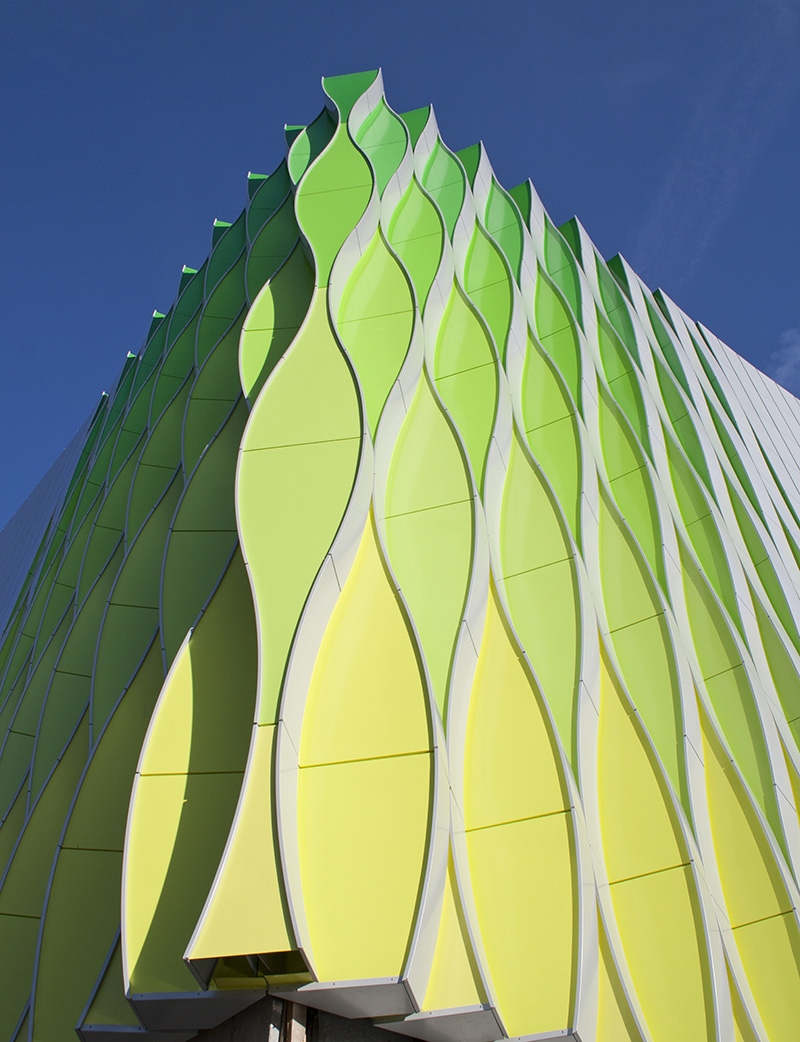
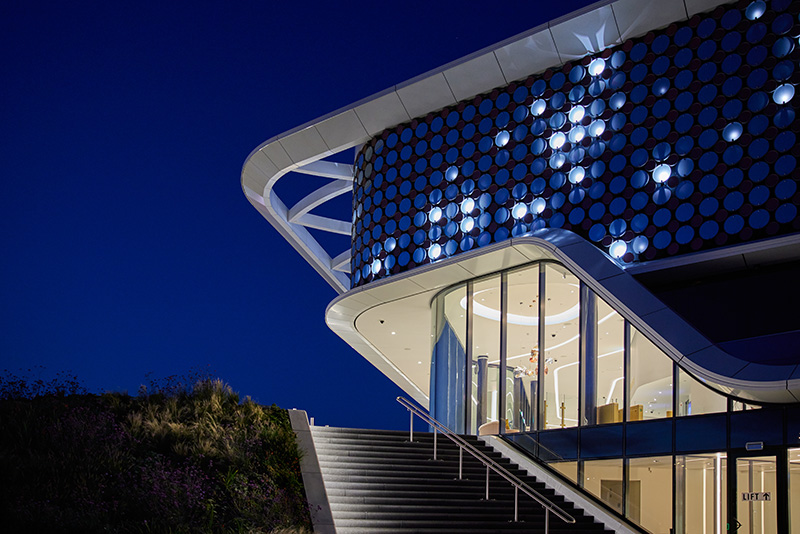
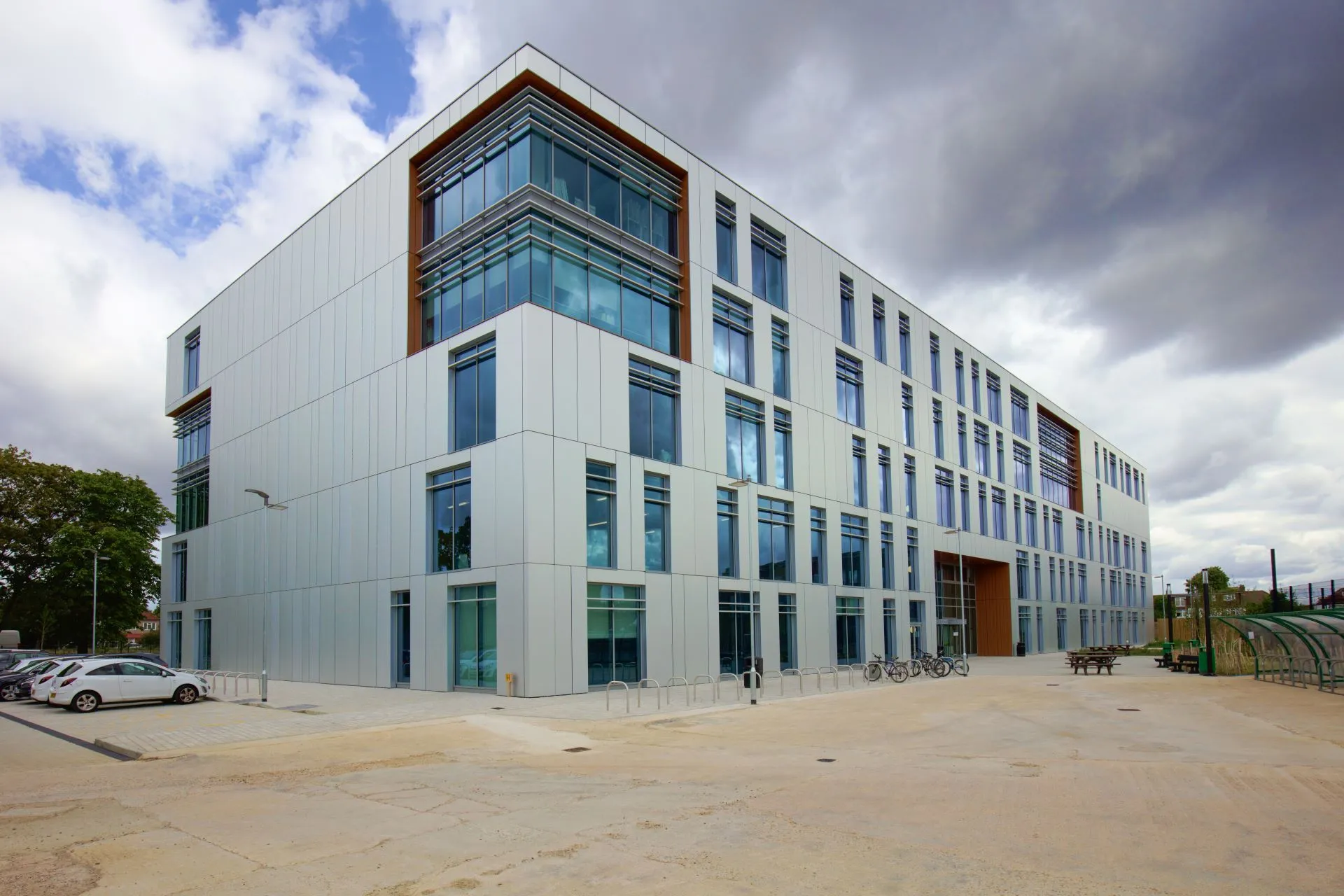
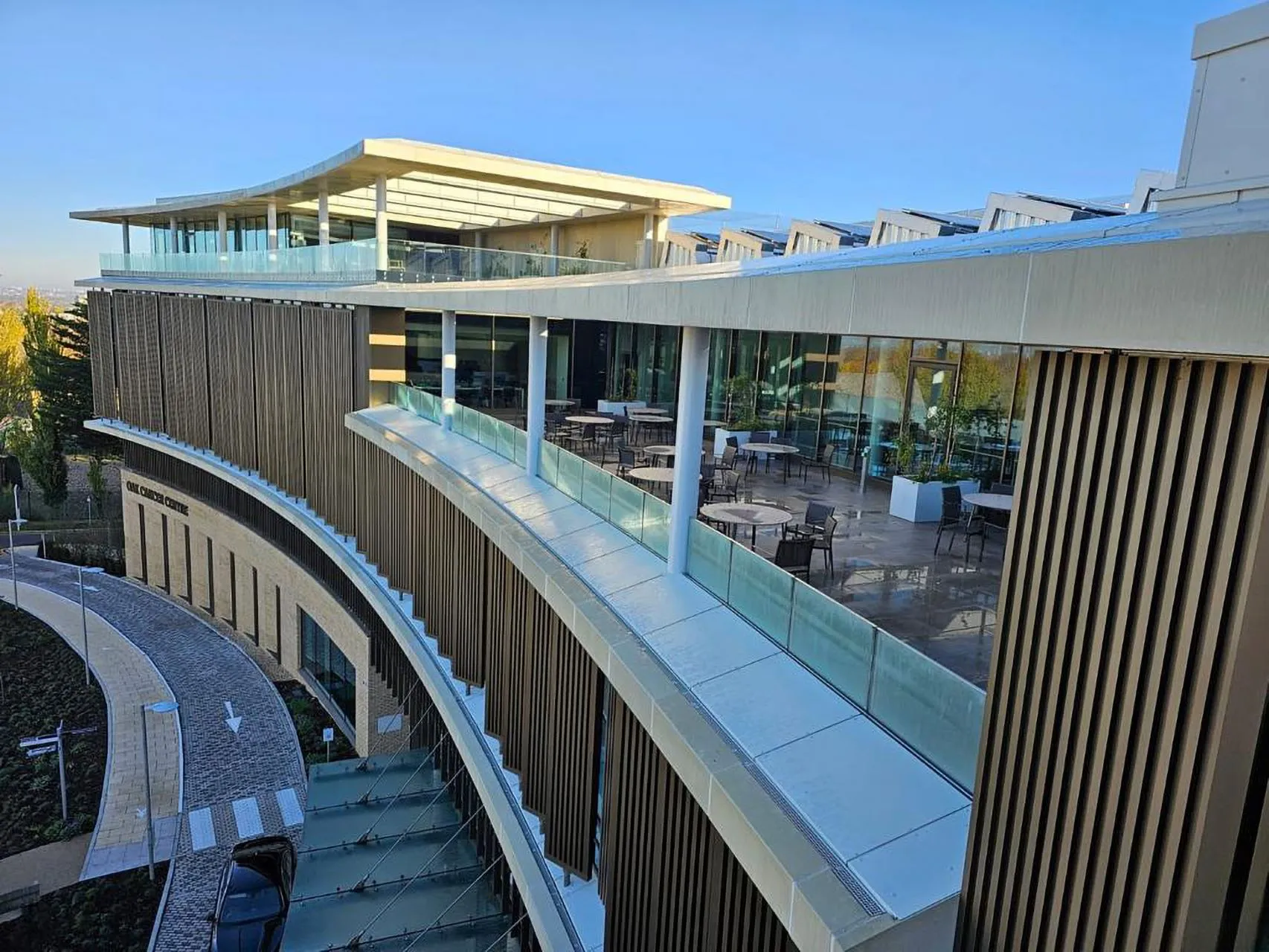
Over Sorba
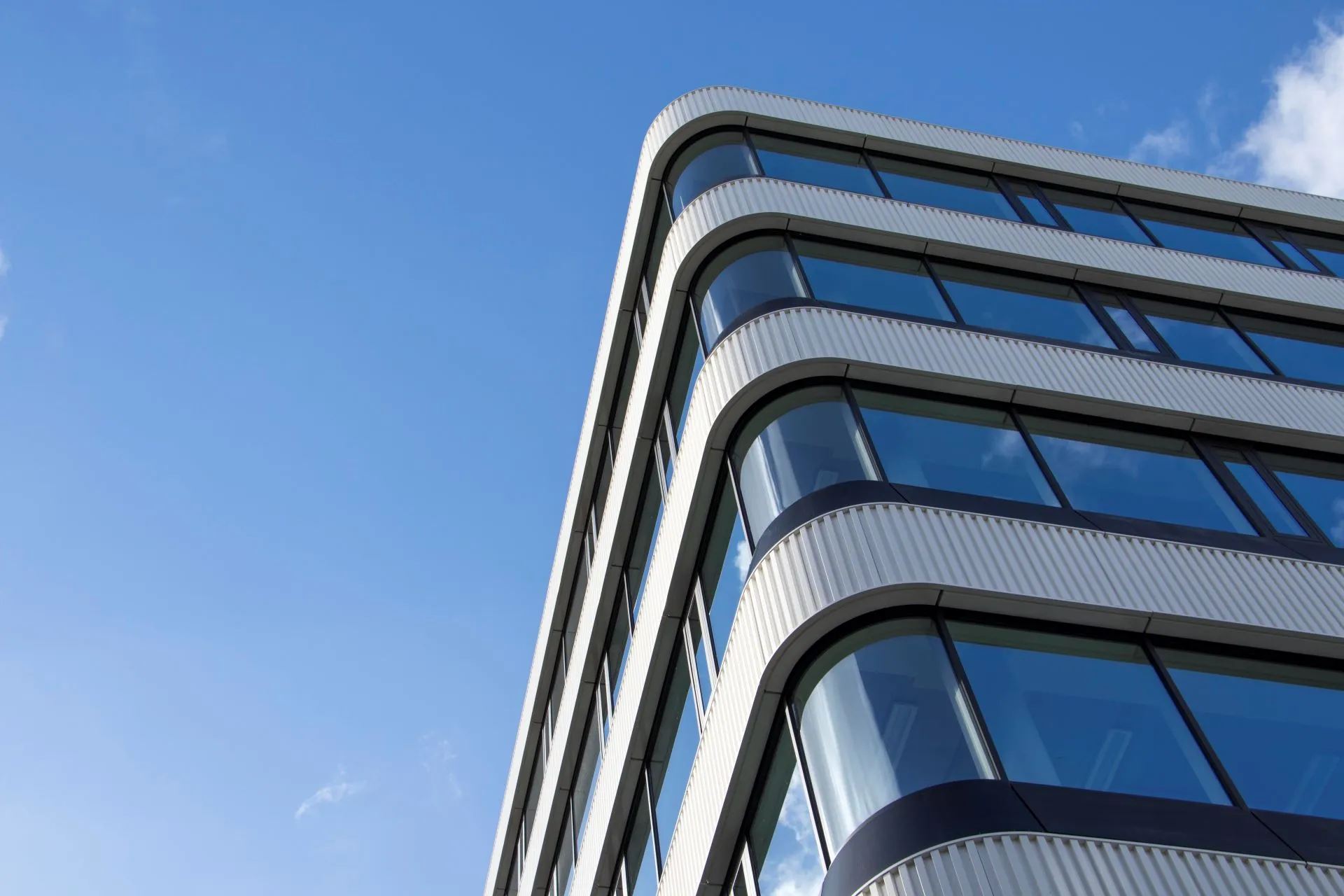
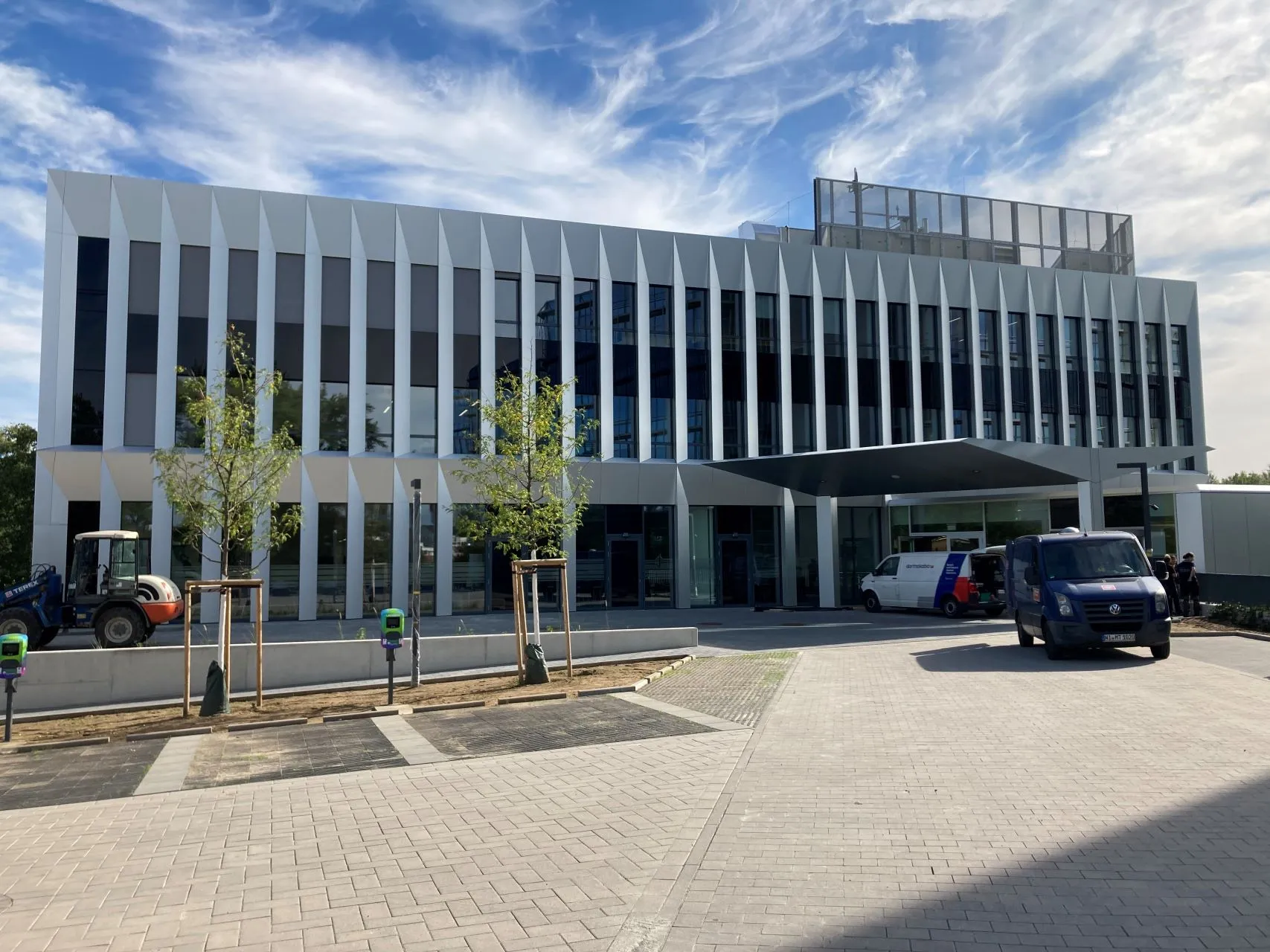
Unieke oppervlakken, markante bouwwerken
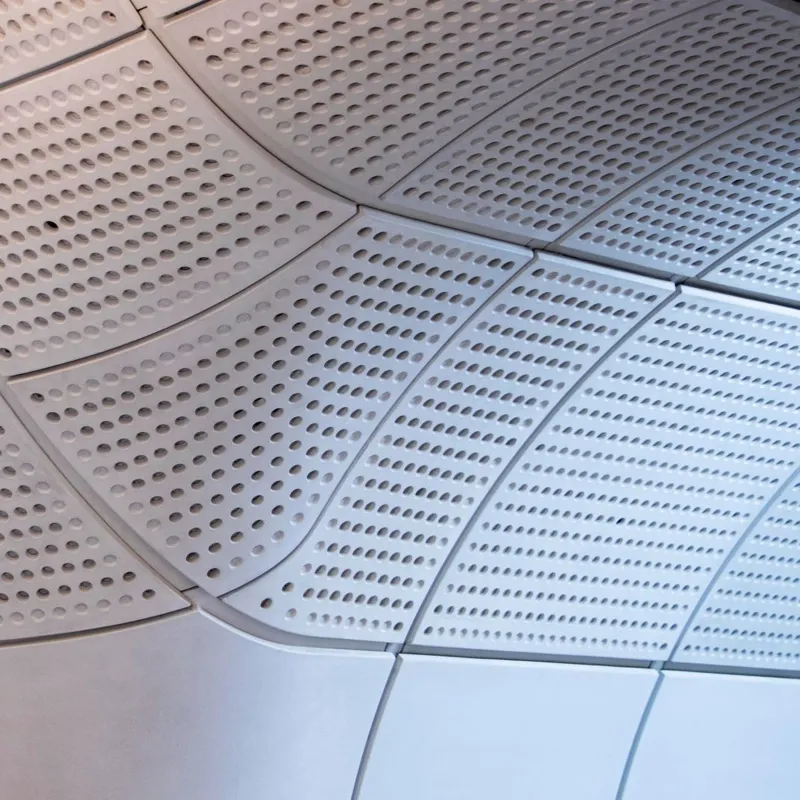
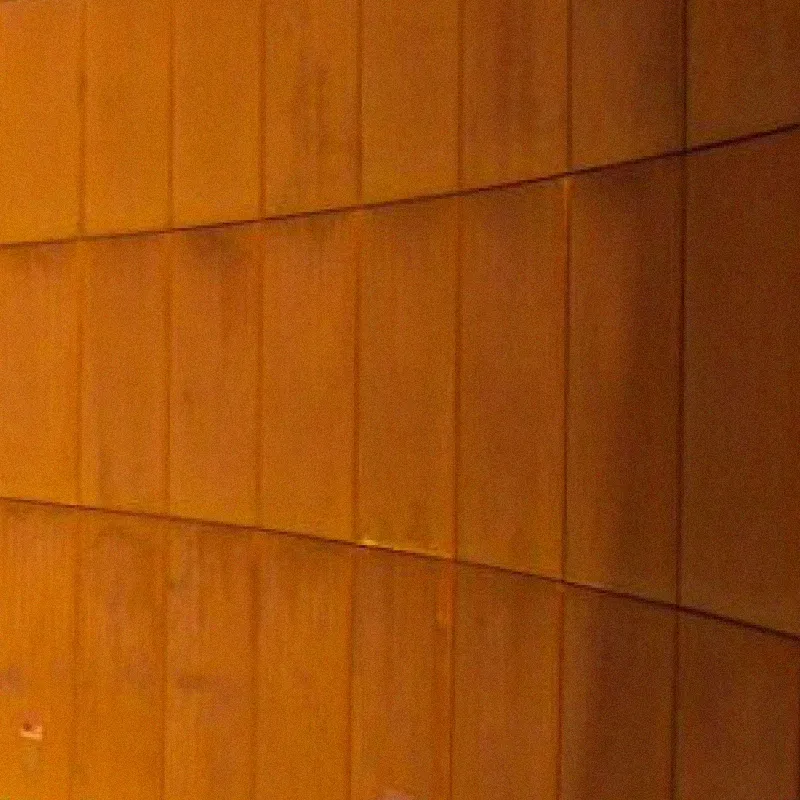
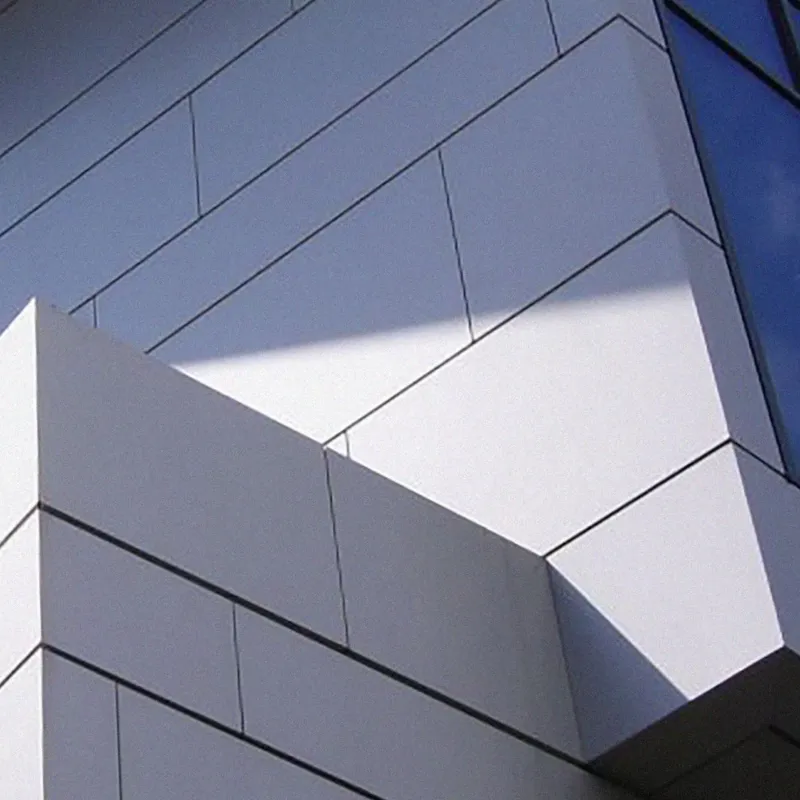
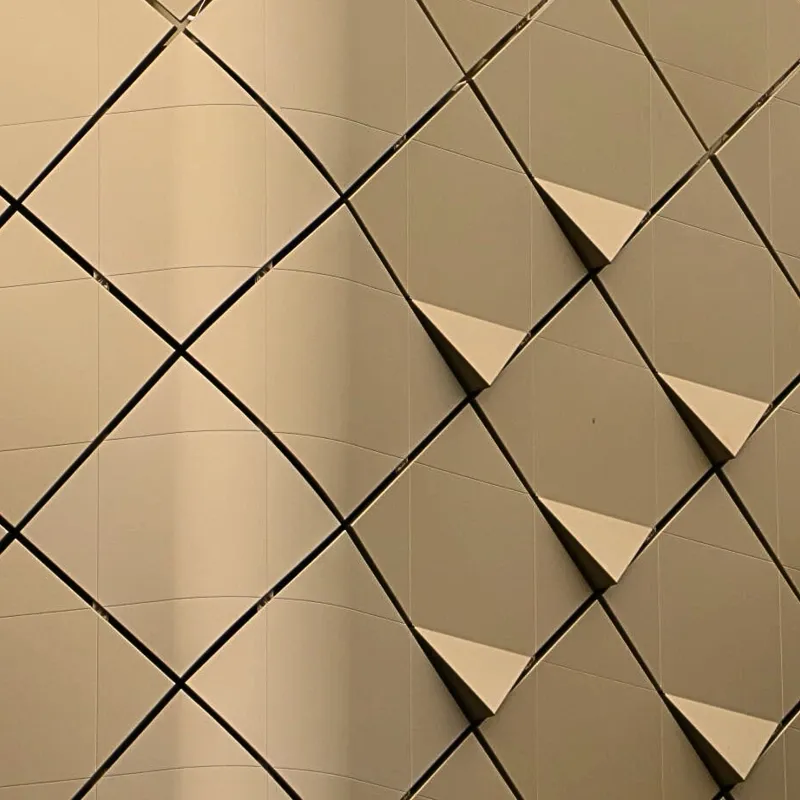
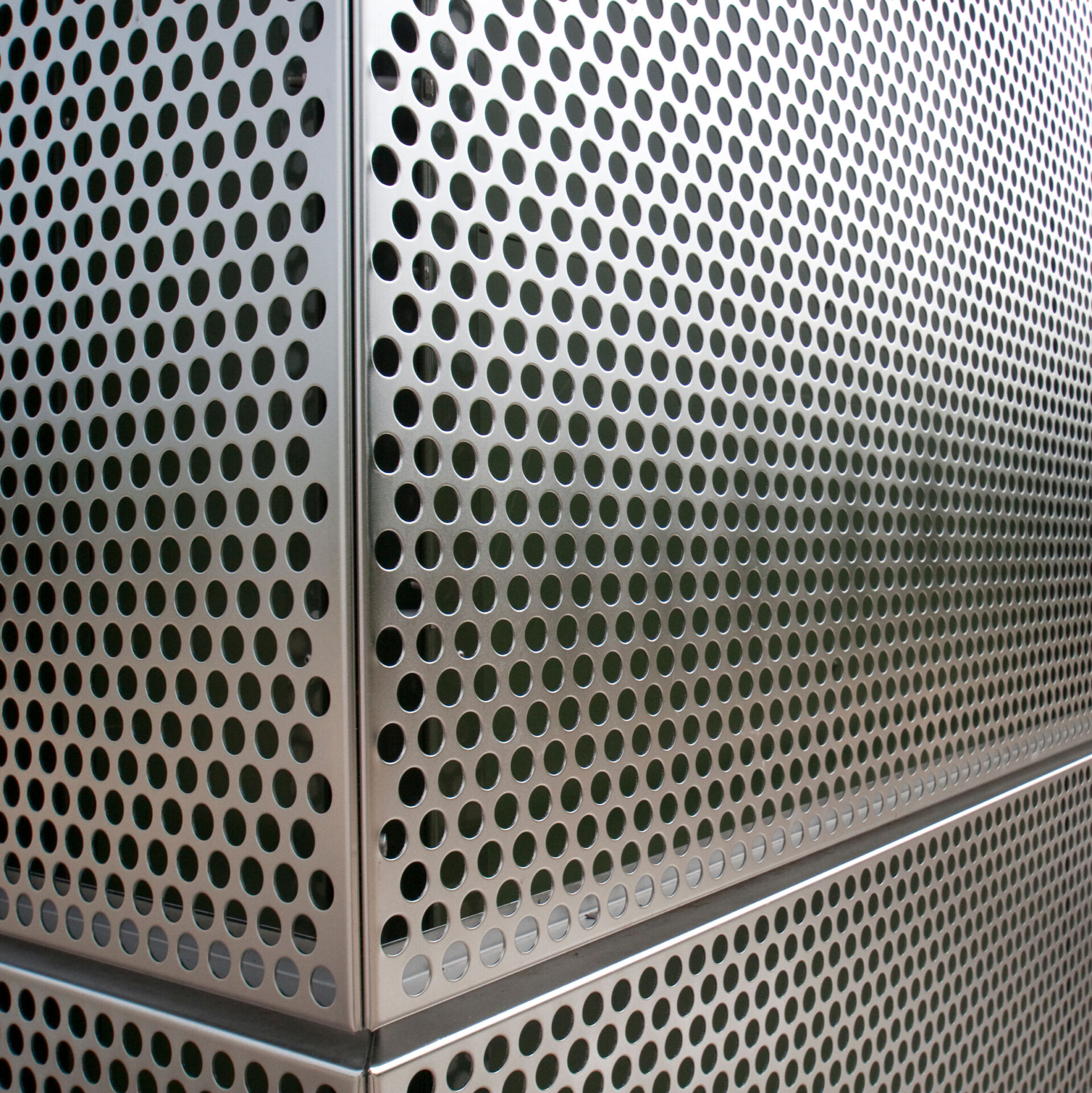
Sorba. Al bijna een halve eeuw een begrip in de wereld van hoogwaardige gevelbekleding en projectbekleding. Onze oorsprong ligt in specialistische plaatbewerking, maar vandaag de dag zijn we een materiaalonafhankelijke fullservice samenwerkingspartner. We werken met en voor architecten, bouwers, inkopers en systeemleveranciers. Sorba is de oplossingsgerichte specialist die de afwerking realiseert waarmee gebouwen en objecten hun allure en esthetiek krijgen.
Materialen en systemen
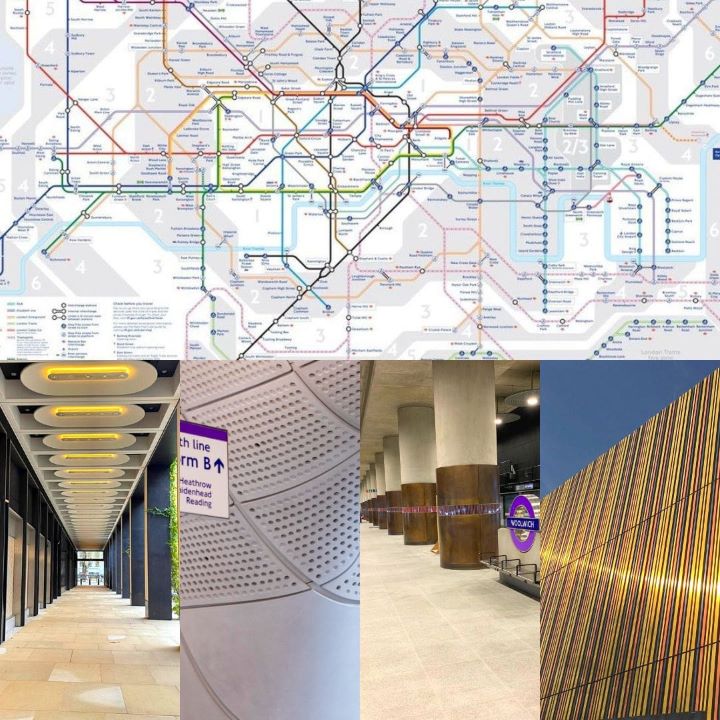
Hier werken wij mee
De veelheid aan materialen en systemen die we in ons repertoire hebben kunnen we niet allemaal hier laten zien. De mogelijkheden zijn simpelweg te uitgebreid. Staat het gewenste materiaal of systeem niet op onze site? Aarzel dan niet om contact met ons op te nemen. Wij staan klaar om samen met u op zoek te gaan naar een passende en unieke oplossing die perfect aansluit op uw specifieke behoeften. De mogelijkheden zijn werkelijk eindeloos, en wij zijn hier om uw visie tot leven te brengen.